

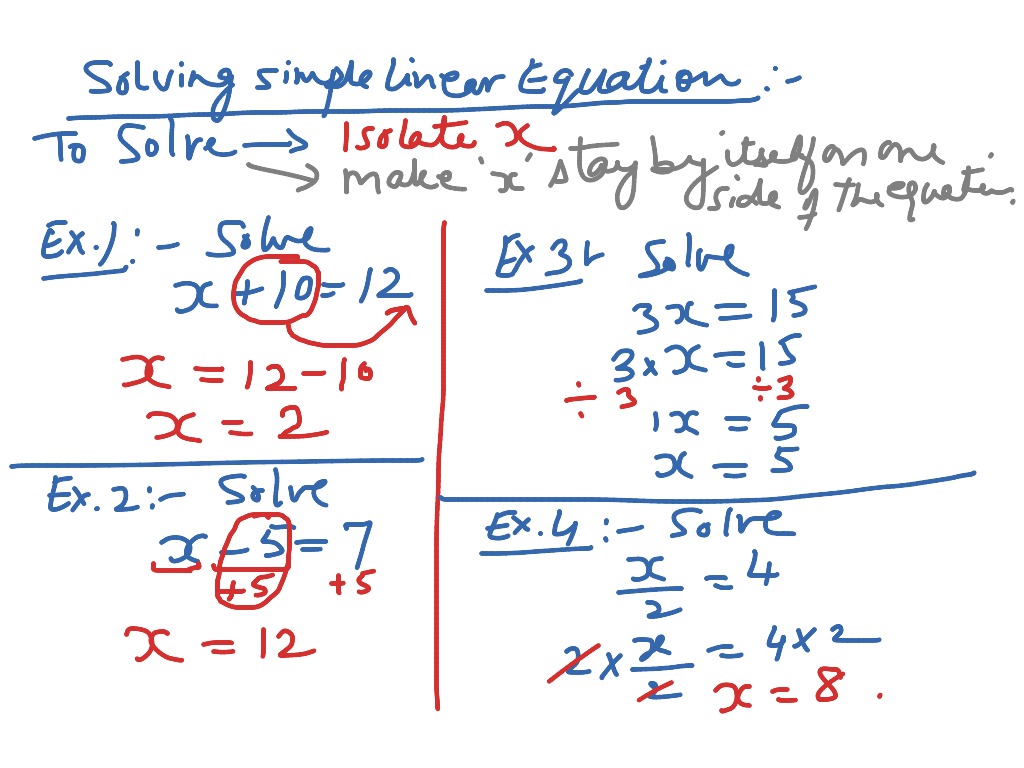
When two or more terms in any algebraic equation are separated by a division sign "/", the algebraic operation performed is division. As you can see in this particular simple equation in mathematics, -20 becomes +20 on the other side.
#Simple math equations plus#
When two or more terms in an algebraic equation are separated by a plus sign "+", the algebraic operation is addition. In each of the algebraic operations performed, we always categorize the terms in our algebraic equations as like and unlike terms. This is distribution of multiplication over addition. The distributive rule of multiplication states that when we multiply a number to addition of two numbers, it results in the output which is same as the sum of their products with the number individually. The equation for the same is written as, a × (b × c) = (a × b) × c. Similarly, the associative rule of multiplication states that when three or more terms are multiplied, the order of multiplication does not matter. For example, x 5 + (3x 2 + 2) = (x 5 + 3x 2) + 2 Associative Rule of Multiplication The equation for the same is written as, a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c. In algebra, the associative rule of addition states that when three or more terms are added, the order of addition does not matter. Here, LHS = RHS, this proves that their values are equal. The equation for the same is written as, (a × b) = (b × a). The commutative rule of multiplication states that when two terms are multiplied, the order of multiplication does not matter.
For example, (x 3 + 2x) = (2x + x 3) Commutative Rule of Multiplication The equation for the same is written as, (a + b) = (b + a). In algebra, the commutative rule of addition states that when two terms are added, the order of addition does not matter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
